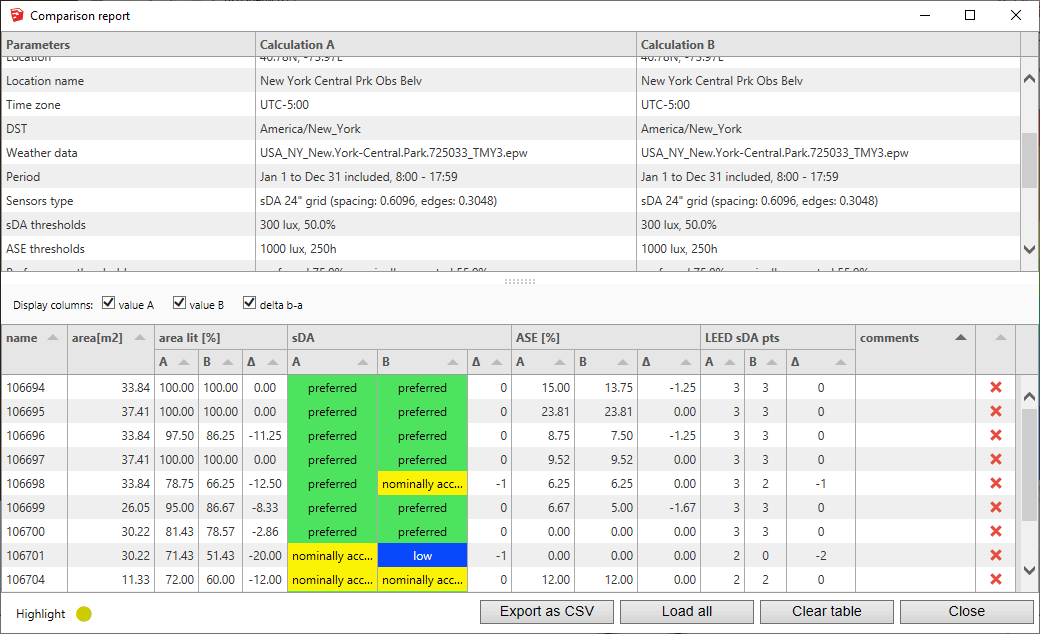
Visualization of sDA results within the model
The results are displayed on the surfaces considering their position regarding the norm
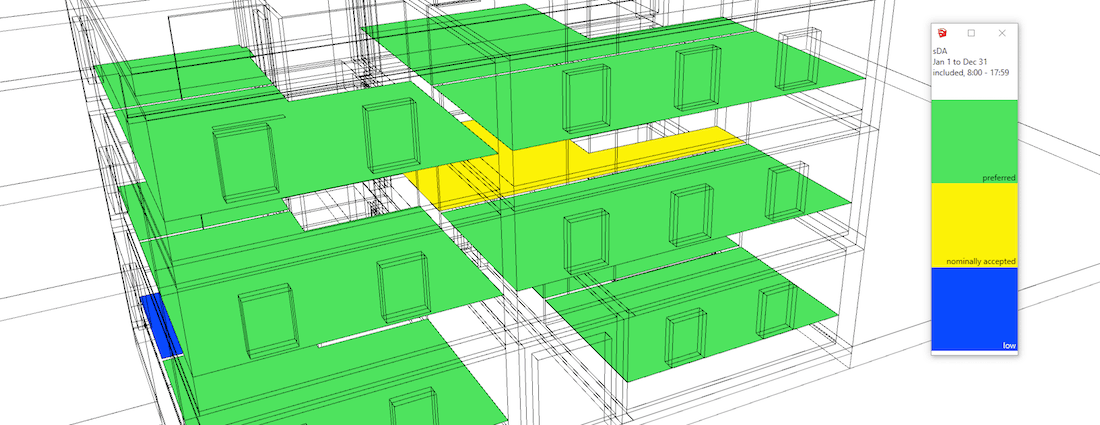
Spatial Daylight Autonomy (sDA) assesses whether a space receives sufficient daylight on a work plane during standard operating hours on an annual basis. The target is 300 lux for 50% of the occupied period.
This extension also calculates the associated indicator ASE (Annual Sunlight Exposure). ASE identifies surfaces receiving too much direct sunlight that may cause visual discomfort (glare) or additional cooling costs. ASE measures the percentage of the work plane exceeding the threshold of 1000 lux more than 250 occupied hours per year.
The sDA and ASE indicators are part of the LEED rating system. They are defined in the IES LM-83-12 standard.
It also calculates the LEED credits.
The results are displayed on the surfaces considering their position regarding the norm

The results are displayed on the surfaces considering their position regarding the norm
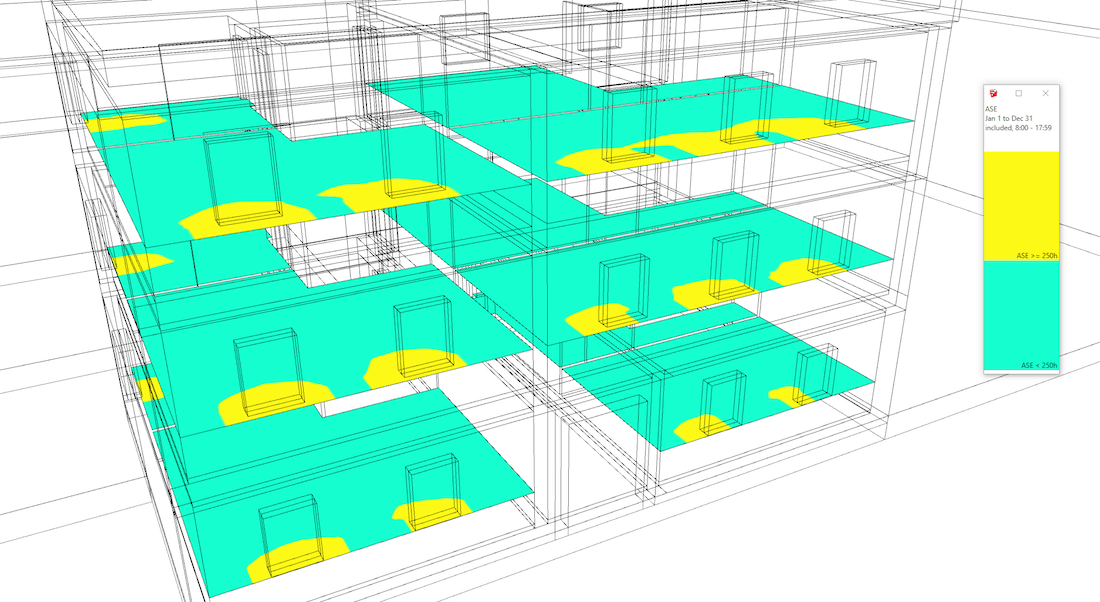
A detailed report
to understand the status of each surface for sDA, ASE and LEED credits
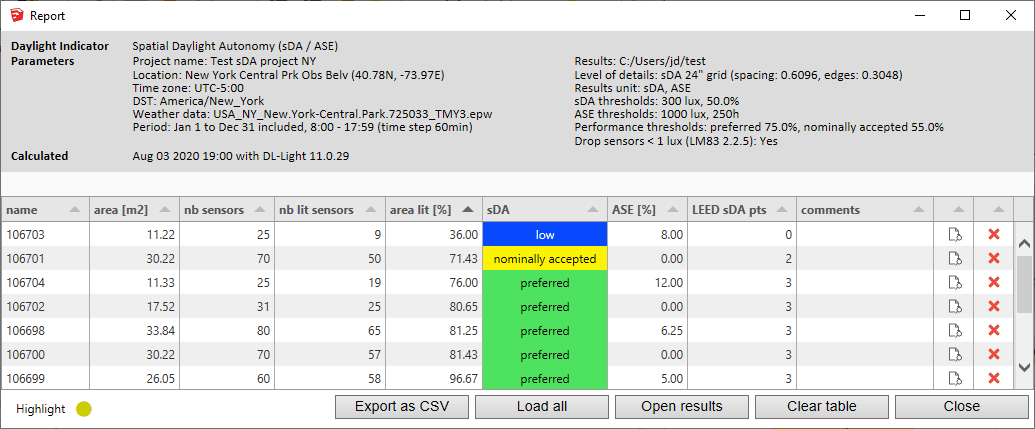
A comparison tool
to understand the impact of choices in the project