In spite of heavy renovations, the spaces in the headquarters of the French National Bnk were felt as tiring, difficult for keeping long term concentration and very uncomfortable.
Users themselves and their management concluded that light played an essential part in this situation.
De Luminæ came to confirm the presence of such discomfort and to find solutions for improvement.
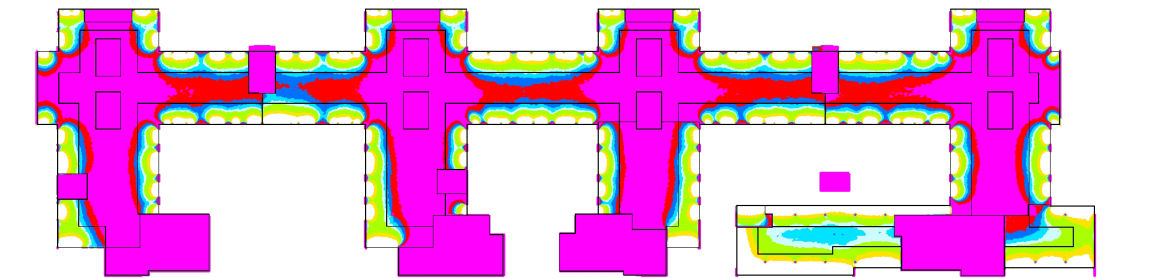
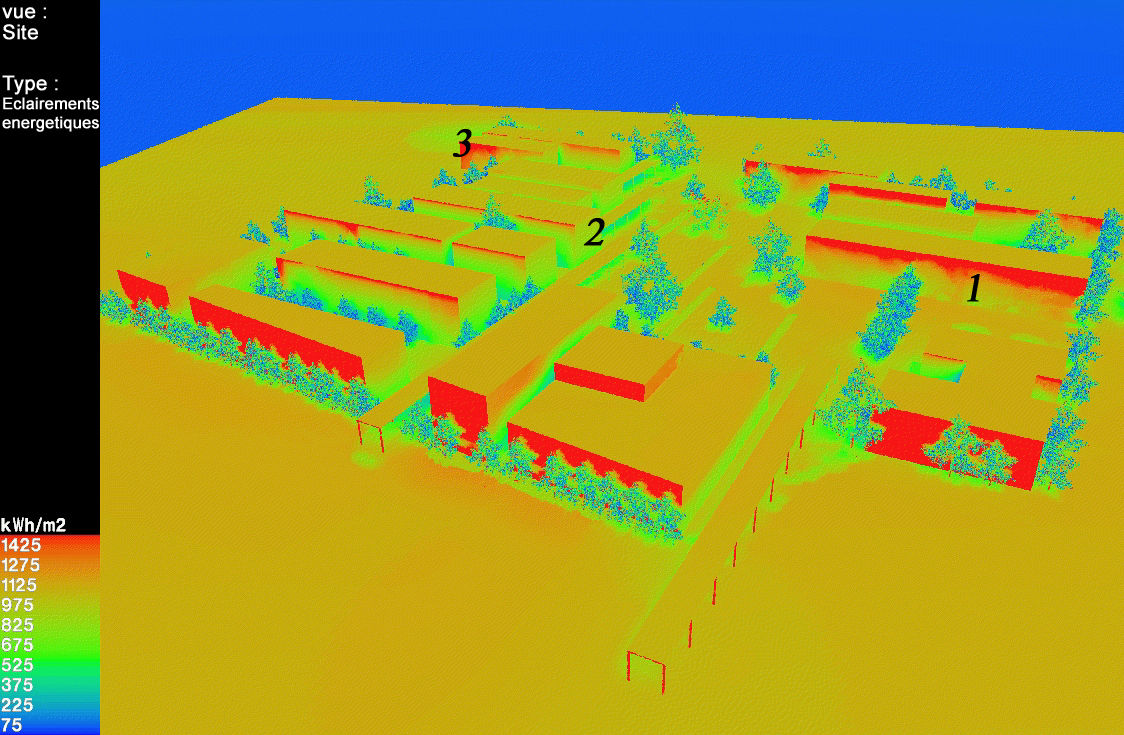
Measurement campaigns of luminance and illuminance due to natural and artificial lighting allowed us to reveal numerous sources of discomfort, small ones, average ones but also extremely strong ones due to the light sources, reflexions on various surfaces, the furniture, the equipements, etc. who were producing uncomfortable and sometimes extreme contrasts.
Simulations of the situation validated these findings and confirmed the results.
De Luminæ proposed various solutions of smaller or bigger magnitude on the elements of the interior (walls, ceiling...) and on very punctual elements like luminaires or equipements.
Meetings with the staff and the management were held to explain the nature of the discomfort and the benefits of the various solutions proposed.